이전 장에서는 대시보드 페이지를 동적으로 만들었지만 느린 데이터 가져오기가 애플리케이션 성능에 어떤 영향을 미칠 수 있는지 논의했다. 데이터 요청이 느린 경우 사용자 경험을 개선할 수 있는 방법을 살펴보겠다.
이번 장에서는 아래의 주제를 다룬다.
- 스트리밍이란 무엇이며 언제 사용할 수 있나?
- loading.tsx 및 Suspense를 사용하여 스트리밍을 구현하는 방법.
- 로딩 스켈레톤이란?
- 경로 그룹은 무엇이며 언제 사용할 수 있나?
- 애플리케이션에서 Suspense 경계를 배치할 위치.
스트리밍이란 무엇입니까?
스트리밍은 경로를 더 작은 "청크"로 나누고 준비가 되면 서버에서 클라이언트로 점진적으로 스트리밍할 수 있는 데이터 전송 기술이다.

스트리밍을 하면 느린 데이터 요청이 전체 페이지를 차단하는 것을 방지할 수 있다. 이를 통해 사용자는 UI가 사용자에게 표시되기 전에 모든 데이터가 로드될 때까지 기다리지 않고 페이지의 일부를 보고 상호 작용할 수 있다.

스트리밍은 각 컴포넌트가 하나의 청크로 간주될 수 있으므로 React의 컴포넌트 모델과 잘 작동한다.
Next.js에서 스트리밍을 구현하는 방법에는 두 가지가 있다.
- 페이지 수준에서 loading.tsx 파일을 사용.
- 특정 컴포넌트의 경우 <Suspense>를 사용.
이것이 어떻게 작동하는지 보자.
loading.tsx를 사용하여 전체 페이지 스트리밍
/app/dashboard 폴더에서 loading.tsx라는 새 파일을 만든다.
/app/dashboard/loading.tsx
export default function Loading() {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
로컬호스트에 다시 접속하면 아래 로딩메시지를 볼 수 있다.

여기서는 일어나는 일은 아래와 같다.
- loading.tsx는 Suspense를 기반으로 구축된 특수 Next.js 파일로, 페이지 콘텐츠가 로드되는 동안 대체 UI로 표시할 폴백 UI를 생성할 수 있다.
- <Sidebar>는 정적이므로 즉시 표시된다. 사용자는 동적 콘텐츠가 로드되는 동안 <Sidebar>와 상호 작용할 수 있다.
- 사용자는 다른 페이지로 이동하기 전에 페이지 로드가 완료될 때까지 기다릴 필요가 없다(이를 중단 가능한 탐색이라고 함).
방금 스트리밍을 구현했다. 하지만 우리는 사용자 경험을 개선하기 위해 더 많은 일을 할 수 있다. 'Loading…' 텍스트 대신 로딩 스켈레톤를 표시해 보자.
로딩 스켈레톤 추가
로딩 스켈레톤은 UI의 단순화된 버전이다. 많은 웹사이트에서는 이를 placeholde로 사용하여 사용자에게 콘텐츠가 로드 중임을 나타낸다. loading.tsx에 포함하는 모든 UI는 정적 파일의 일부로 포함되어 먼저 전송된다. 그런 다음 나머지 동적 콘텐츠가 서버에서 클라이언트로 스트리밍된다.
loading.tsx 파일 내에서 <DashboardSkeleton>이라는 새 컴포넌트를 가져온다.
/app/dashboard/loading.tsx
import DashboardSkeleton from '@/app/ui/skeletons';
export default function Loading() {
return <DashboardSkeleton />;
}
localhost 를 다시 접속해서 리프레시하면 아래와 같이 보일 것이다.

route group(경로 그룹) 을 이용한 로딩 스켈레톤 버그 수정
현재 로딩 스켈레톤은 송장 및 고객 페이지에도 적용된다.
loading.tsx는 파일 시스템의 /invoices/page.tsx 및 /customers/page.tsx보다 높은 수준이므로 해당 페이지에도 적용된다.
Route Groups(경로 그룹)를 사용하여 이를 변경할 수 있다. 대시보드 폴더 내에 /(overview)라는 새 폴더를 만든다. 그런 다음 loading.tsx 및 page.tsx 파일을 폴더 내로 이동한다.
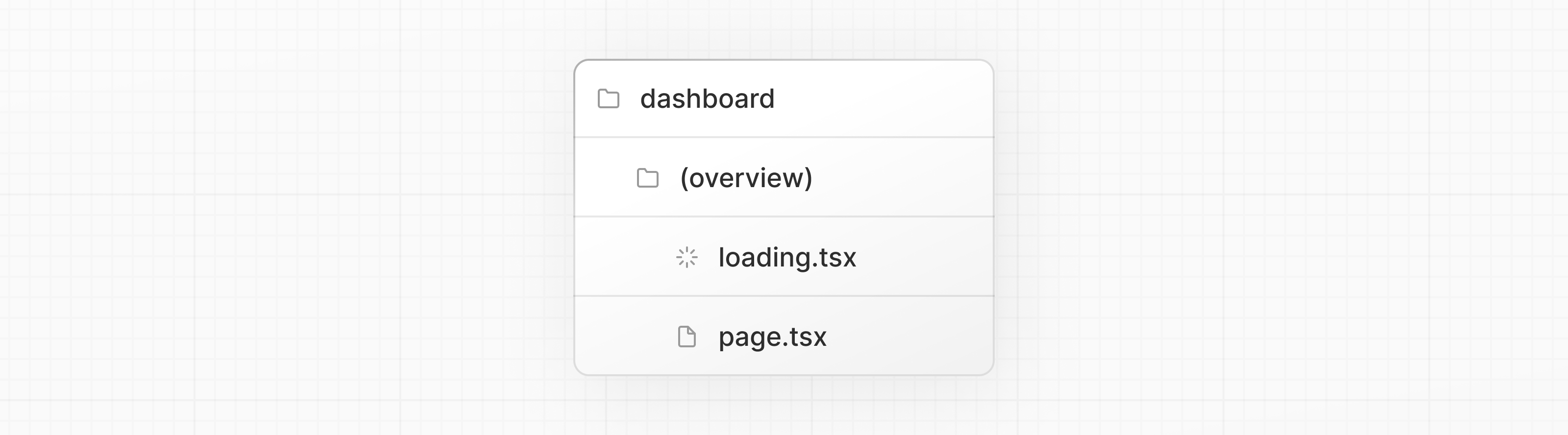
이제 loading.tsx 파일은 대시보드 overview 페이지에만 적용됩니다.
경로 그룹을 사용하면 URL 경로 구조에 영향을 주지 않고 파일을 논리적 그룹으로 구성할 수 있다. 괄호()를 사용하여 새 폴더를 생성하면 해당 이름이 URL 경로에 포함되지 않는다. 따라서 /dashboard/(overview)/page.tsx는 /dashboard가 된다.
여기서는 loading.tsx가 대시보드 개요 페이지에만 적용되도록 경로 그룹을 사용하고 있다. 그러나 경로 그룹을 사용하여 애플리케이션을 섹션(예: (marketing) 경로 및 (shopping) 경로)으로 분리하거나 대규모 애플리케이션의 경우 팀별로 분리할 수도 있다.
컴포넌트 스트리밍
지금까지는 전체 페이지를 스트리밍하고 있다. React Suspense를 사용하면 더욱 세분화되고 특정 컴포넌트를 스트리밍할 수 있다.
Suspense를 사용하면 일부 조건이 충족될 때까지(예: 데이터 로드) 애플리케이션의 렌더링 부분을 연기할 수 있다. Suspense에서 동적 컴포넌트를 래핑할 수 있다. 그런 다음 동적 컴포넌트가 로드되는 동안 표시할 대체 컴포넌트를 전달한다.
느린 데이터 요청인 fetchRevenue()를 기억하신다면 이는 전체 페이지의 속도를 늦추는 요청이다. 페이지를 차단하는 대신 Suspense를 사용하여 이 컴포넌트만 스트리밍하고 페이지 UI의 나머지 부분을 즉시 표시할 수 있었다.
이렇게 하려면 가져온 데이터를 컴포넌트로 이동해야 한다. 코드를 업데이트하여 어떻게 보이는지 살펴보자.
/dashboard/(overview)/page.tsx에서 fetchRevenue()의 모든 인스턴스와 해당 데이터를 삭제한다.
/app/dashboard/(overview)/page.tsx
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchLatestInvoices, fetchCardData } from '@/app/lib/data'; // remove fetchRevenue
export default async function Page() {
const revenue = await fetchRevenue // delete this line
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices();
const {
numberOfInvoices,
numberOfCustomers,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData();
return (
// ...
);
}
그 다음 React에서 <Suspense>를 가져와서 <RevenueChart />로 감싸자. <RevenueChartSkeleton>이라는 대체 컴포넌트를 전달할 수 있다.
/app/dashboard/(overview)/page.tsx
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchLatestInvoices, fetchCardData } from '@/app/lib/data';
import { Suspense } from 'react';
import { RevenueChartSkeleton } from '@/app/ui/skeletons';
export default async function Page() {
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices();
const {
numberOfInvoices,
numberOfCustomers,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData();
return (
<main>
<h1 className={`${lusitana.className} mb-4 text-xl md:text-2xl`}>
Dashboard
</h1>
<div className="grid gap-6 sm:grid-cols-2 lg:grid-cols-4">
<Card title="Collected" value={totalPaidInvoices} type="collected" />
<Card title="Pending" value={totalPendingInvoices} type="pending" />
<Card title="Total Invoices" value={numberOfInvoices} type="invoices" />
<Card
title="Total Customers"
value={numberOfCustomers}
type="customers"
/>
</div>
<div className="mt-6 grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 md:grid-cols-4 lg:grid-cols-8">
<Suspense fallback={<RevenueChartSkeleton />}>
<RevenueChart />
</Suspense>
<LatestInvoices latestInvoices={latestInvoices} />
</div>
</main>
);
}
마지막으로 <RevenueChart> 컴포넌트를 업데이트하여 자체 데이터를 가져오고 전달된 prop을 제거한다.
/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart.tsx
import { generateYAxis } from '@/app/lib/utils';
import { CalendarIcon } from '@heroicons/react/24/outline';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchRevenue } from '@/app/lib/data';
// ...
export default async function RevenueChart() { // Make component async, remove the props
const revenue = await fetchRevenue(); // Fetch data inside the component
const chartHeight = 350;
const { yAxisLabels, topLabel } = generateYAxis(revenue);
if (!revenue || revenue.length === 0) {
return <p className="mt-4 text-gray-400">No data available.</p>;
}
return (
// ...
);
}
이제 페이지를 새로 고치면 대시보드 정보가 거의 즉시 표시되고 <RevenueChart>에 대한 대체 스켈레톤이 표시된다.

연습: 스트리밍 <LatestInvoices>
<LatestInvoices> 컴포넌트를 스트리밍하여 방금 배운 내용을 연습해 보자.
fetchLatestInvoices()를 페이지에서 <LatestInvoices> 컴포넌트로 이동한다. <LatestInvoicesSkeleton>이라는 폴백을 사용하여 <Suspense> 경계에 컴포넌트를 래핑한다.
해결된 코드는 아래와 같다.
/app/dashboard/(overview)/page.tsx
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchCardData } from '@/app/lib/data'; // Remove fetchLatestInvoices
import { Suspense } from 'react';
import {
RevenueChartSkeleton,
LatestInvoicesSkeleton,
} from '@/app/ui/skeletons';
export default async function Page() {
// Remove `const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices()`
const {
numberOfInvoices,
numberOfCustomers,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData();
return (
<main>
<h1 className={`${lusitana.className} mb-4 text-xl md:text-2xl`}>
Dashboard
</h1>
<div className="grid gap-6 sm:grid-cols-2 lg:grid-cols-4">
<Card title="Collected" value={totalPaidInvoices} type="collected" />
<Card title="Pending" value={totalPendingInvoices} type="pending" />
<Card title="Total Invoices" value={numberOfInvoices} type="invoices" />
<Card
title="Total Customers"
value={numberOfCustomers}
type="customers"
/>
</div>
<div className="mt-6 grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 md:grid-cols-4 lg:grid-cols-8">
<Suspense fallback={<RevenueChartSkeleton />}>
<RevenueChart />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<LatestInvoicesSkeleton />}>
<LatestInvoices />
</Suspense>
</div>
</main>
);
}
<LatestInvoices> 컴포넌트에서 속성을 제거하는 것을 잊지 말자!
/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices.tsx
import { ArrowPathIcon } from '@heroicons/react/24/outline';
import clsx from 'clsx';
import Image from 'next/image';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchLatestInvoices } from '@/app/lib/data';
export default async function LatestInvoices() { // Remove props
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices();
return (
// ...
);
}
컴포넌 그룹화
이제 거의 다 왔다. 이제 Suspense에서 <Card> 컴포넌트를 래핑하자. 각 개별 카드에 대한 데이터를 가져올 수 있지만 이로 인해 카드가 로드될 때 팝업 효과가 발생할 수 있으며 이는 사용자에게 시각적으로 불편할 수 있다.
그렇다면 이 문제를 어떻게 해결할까?
더 많은 시차 효과를 생성하려면 래퍼 컴포넌트를 사용하여 카드를 그룹화할 수 있습니다. 즉, 정적 <Sidebar/>가 먼저 표시되고 그다음에 카드 등이 표시된다.
page.tsx 파일에서:
- <Card> 컴포넌트를 삭제한다.
- fetchCardData() 함수를 삭제한다.
- <CardWrapper />라는 새 래퍼 컴포넌트를 가져온다.
- <CardsSkeleton />이라는 새 스켈레톤 컴포넌트를 가져온다.
- <CardWrapper />를 Suspense로 래핑한다.
/app/dashboard/page.tsx
import CardWrapper from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
// ...
import {
RevenueChartSkeleton,
LatestInvoicesSkeleton,
CardsSkeleton,
} from '@/app/ui/skeletons';
export default async function Page() {
return (
<main>
<h1 className={`${lusitana.className} mb-4 text-xl md:text-2xl`}>
Dashboard
</h1>
<div className="grid gap-6 sm:grid-cols-2 lg:grid-cols-4">
<Suspense fallback={<CardsSkeleton />}>
<CardWrapper />
</Suspense>
</div>
// ...
</main>
);
}그 다음 /app/ui/dashboard/cards.tsx 파일로 이동하고 fetchCardData() 함수를 가져온 다음 <CardWrapper/> 컴포넌트내에서 호출한다. 이 컴포넌트에서 필요한 코드의 주석 처리를 제거했는지 확인하자.
/app/ui/dashboard/cards.tsx
// ...
import { fetchCardData } from '@/app/lib/data';
// ...
export default async function CardWrapper() {
const {
numberOfInvoices,
numberOfCustomers,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData();
return (
<>
<Card title="Collected" value={totalPaidInvoices} type="collected" />
<Card title="Pending" value={totalPendingInvoices} type="pending" />
<Card title="Total Invoices" value={numberOfInvoices} type="invoices" />
<Card
title="Total Customers"
value={numberOfCustomers}
type="customers"
/>
</>
);
}페이지를 새로 고치면 모든 카드가 동시에 로드되는 것을 볼 수 있다. 여러 컴포넌트를 동시에 로드하려는 경우 이 패턴을 사용할 수 있을 것이다.
Suspense 경계를 배치할 위치 결정
Suspense 경계를 배치하는 위치는 다음 몇 가지 사항에 따라 달라진다.
- 페이지가 스트리밍될 때 사용자가 페이지를 경험하기를 원하는 방식이다.
- 어떤 콘텐츠에 우선순위를 두고 싶은지.
- 컴포넌트가 데이터 페치에 의존하는 경우
대시보드 페이지를 살펴자. 다르게 수행했을 만한 작업이 있는가?
정답은 없다.
- loading.tsx에서 했던 것처럼 전체 페이지를 스트리밍할 수 있지만 컴포넌트 중 하나의 데이터 가져오기 속도가 느린 경우 로드 시간이 더 길어질 수 있다.
- 모든 컴포넌트를 개별적으로 스트리밍할 수 있지만 UI가 준비되면 화면에 갑자기 나타날 수 있다.
- 페이지 섹션을 스트리밍하여 시차 효과를 만들 수도 있다. 하지만 래퍼 컴포넌트를 만들어야 한다.
서스펜스 경계를 배치하는 위치는 애플리케이션에 따라 달라진다. 일반적으로 데이터 가져오기를 필요한 컴포넌트로 이동한 다음 Suspense에서 해당 컴포넌트를 래핑하는 것이 좋다. 그러나 애플리케이션에 필요한 경우 섹션이나 전체 페이지를 스트리밍하는 데 아무런 문제가 없다.
Suspense를 실험해보고 가장 효과적인 것이 무엇인지 알아보자. Suspense는 보다 즐거운 사용자 경험을 만드는 데 도움이 될 수 있는 강력한 API 이다.
다음으로는
스트리밍 및 서버 컴포넌트는 궁극적으로 최종 사용자 경험을 개선한다는 목표를 가지고 데이터 가져오기 및 로드 상태를 처리하는 새로운 방법을 제공한다.
다음 장에서는 스트리밍을 염두에 두고 구축된 새로운 Next.js 렌더링 모델인 부분 사전 렌더링에 대해 알아본다.
'Next.js 개발 가이드 > 06. Learn Next.js 공식 가이드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 11. 검색, 페이지네이션 (0) | 2023.12.24 |
|---|---|
| 10. 부분 사전 렌더링(Partial Prerendering - Optional) (0) | 2023.12.23 |
| 08. 정적 렌더링, 동적 렌더링 (0) | 2023.12.23 |
| 07. 데이터 통신 (0) | 2023.12.23 |
| 06. 데이터베이스 설정 (0) | 2023.12.23 |



